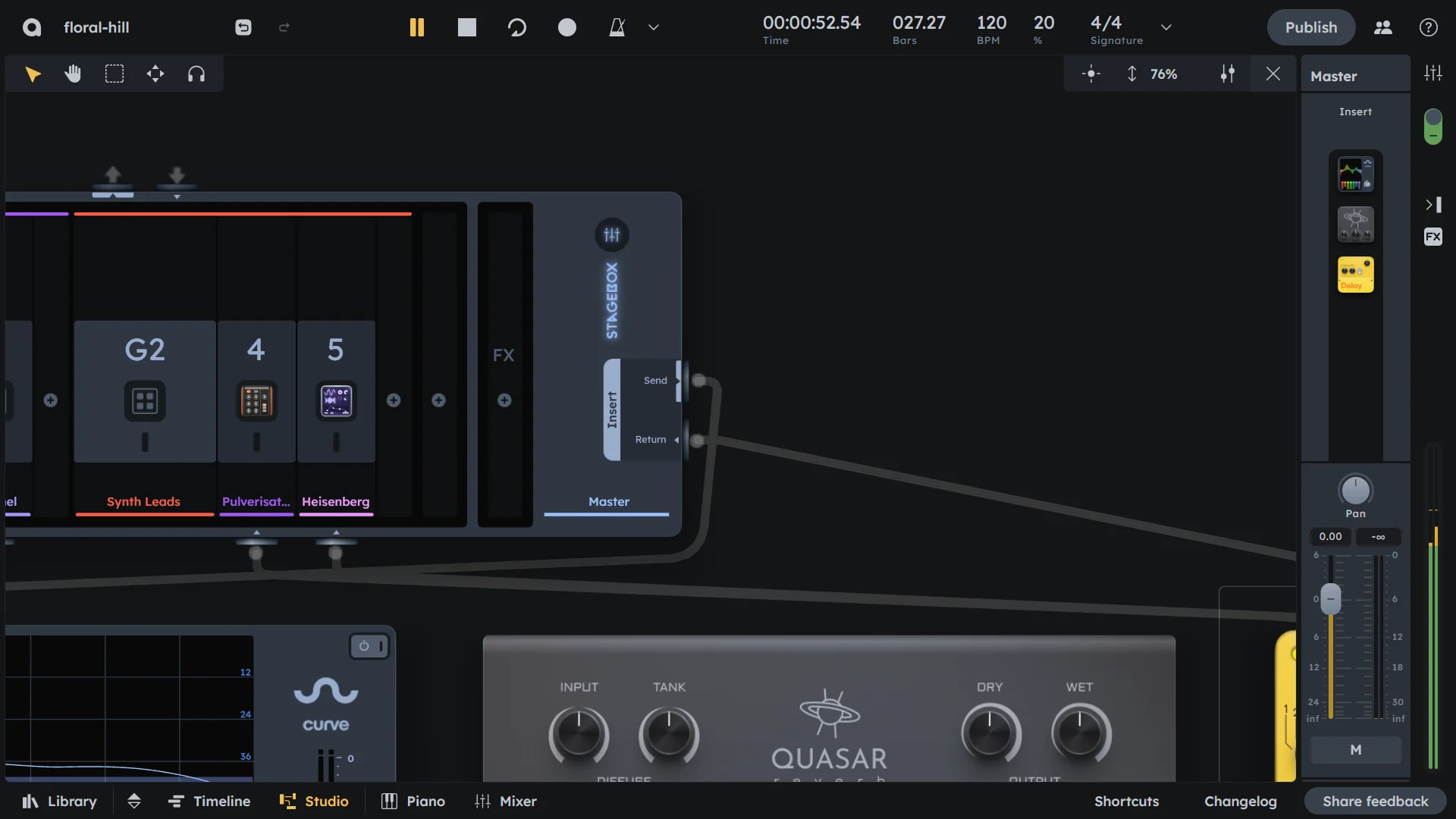
Master
Essentials
Master channel is the final stage where all audio converges before output. Use it to apply final processing (like mastering EQ or compression), control overall mix volume, and ensure your mix doesn’t clip. The built-in limiter prevents clipping while maintaining loudness.
Master insert for final effects processing (mastering EQ, compression, etc.)
Built-in limiter to prevent clipping
Master volume fader for overall level
Final output destination
Controls
The master channel provides final processing and output control for your entire mix.
Master Insert |
Optional custom effects processing chain via the Stagebox (see Stagebox). |
|---|---|
Limiter |
Built-in limiter to prevent clipping. It introduces noticable latency when enabled, so it is disabled by default. |
Volume & Pan |
Controls the final output level and stereo positioning of the mix (see Volume & Pan). |
Mastering
Pre-Mastering
Before applying master processing:
Mix balance |
Ensure all elements are properly balanced. |
|---|---|
Frequency balance |
Check that no frequencies are too prominent or missing. |
Dynamic range |
Ensure good contrast between loud and quiet parts. |
Stereo image |
Verify proper left/right balance and width. |
Master Processing Chain
Typical master processing order:
EQ - Subtle frequency adjustments for overall balance.
Compression - Light compression to glue the mix together.
Stereo Enhancement - Widen or focus the stereo image.
Harmonic Enhancement - Add warmth and character.
Limiting - Final peak limiting to prevent clipping.
Mastering Tips
Level Management
Headroom |
Leave 3-6 dB of headroom before mastering. |
|---|---|
Peak levels |
Keep peaks below -3 dB to avoid clipping. |
RMS levels |
Aim for consistent RMS levels across your mix. |
Reference |
Compare your levels to commercial releases. |
Frequency Balance
Low end |
Ensure bass frequencies are balanced and not overwhelming. |
|---|---|
Midrange |
Check that vocals and instruments sit well in the mix. |
High end |
Verify that high frequencies are present but not harsh. |
Overall balance |
Use spectrum analysis to check frequency distribution. |
Dynamic Control
Compression |
Use light compression to glue elements together. |
|---|---|
Limiting |
Apply limiting sparingly to avoid over-compression. |
Consistency |
Ensure consistent levels throughout the song. |
Practical Tips
Practical Tips
Keep master fader at 0 dB and mix with individual channel faders.
Use the master insert for subtle mastering effects, not heavy processing.
Enable the limiter only when necessary to avoid unwanted latency.
Reference commercial tracks at similar volume levels while mastering.
Apply master processing conservatively - less is often more.