Space
Essentials
Space is a spectrum-based wavetable synthesizer with two blendable slots (A/B), envelopes, LFO, tuning, stereo tools and performance modes. Perfect for evolving pads, textures, and animated leads.
Spectrum-based wavetable synthesis
Two blendable slots (A/B)
Envelopes, LFO, and tuning
Stereo tools and performance modes
Hint
What is a wavetable synthesizer?
A wavetable synthesizer generates sound by playing back digitally stored waveforms (“wavetables”). Each wavetable consists of multiple harmonics (called “partials”) that define the sound’s character. The Space Synth can load two wavetables simultaneously (Slot A and B) and blend between them to create rich and evolving sounds.
Tools

Reset |
Resets the spectrum to a neutral state |
|---|---|
Randomize |
Generates a random spectrum—great for creative inspiration |
Copy to A/B |
Copies the spectrum from one slot to the other |
Swap |
Swaps the contents of Slot A and B |
These tools allow quick experimentation without losing your current setup.
Spectrum/Comb
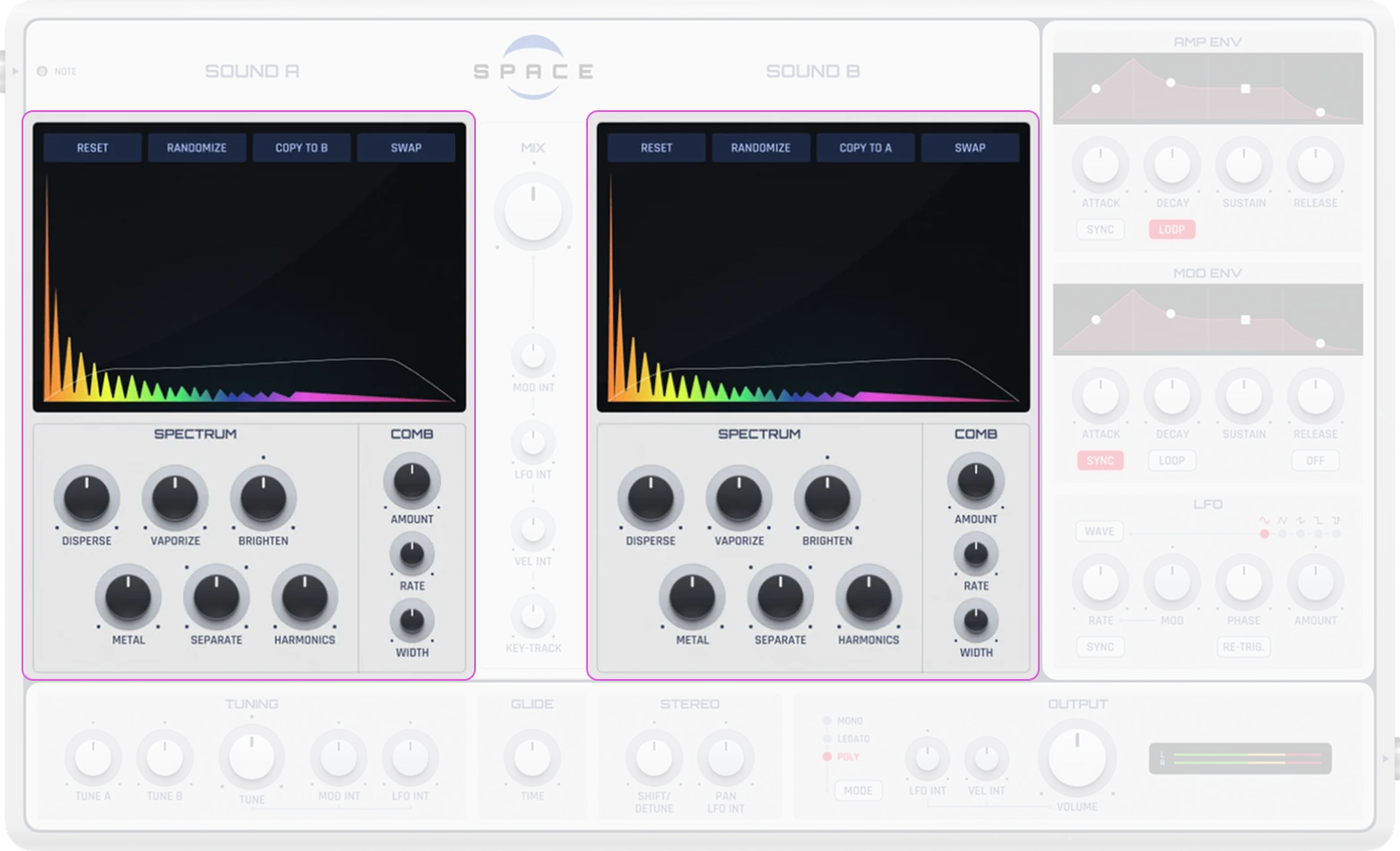
Partials |
Vertical lines that represent the amplitude of individual frequency components. More partials = a more complex sound |
|---|---|
Bandwidth |
Controls the width of the partials. Wider bandwidth results in a softer sound, narrower bandwidth produces sharper, more focused tones |
Brightness |
Controls the brightness quality of the sound (0-100%) |
Dispersion |
Affects the spectral dispersion of the sound (0-100%) |
Metal |
Controls the metallic quality of the sound (0-100%) |
Separation |
Affects the separation between partials (0-100%) |
Vaporisation |
Controls the “vaporization” quality of the sound (0-100%) |
Harmonics Count |
Number of harmonics in the spectrum (1-4) |
Comb Filter Amount |
Controls comb filtering on the sound’s overtones (0-100%) |
Comb Filter Rate |
Rate of the comb filter modulation (0-100%) |
Comb Filter Width |
Width of the comb filter effect (0-100%) |
You can click and drag within the spectrum window to emphasize or reduce specific frequencies.
Wavetable A/B & Mix

Wavetable A and B |
Two independent sound sources with separate spectrums |
|---|---|
Mix (Mix A/B) |
Adjusts the blend between wavetables A and B (-100% to 100%). -100% = only A, 0% = equal mix, 100% = only B |
Envelopes

Amp Envelope |
Controls the amplitude (volume) of the sound over time. Standard ADSR envelope |
|---|---|
Mod Envelope |
Can be assigned to modulate almost any parameter (e.g., LFO rate, mix, pitch, gain). Standard ADSR envelope |
Mod Envelope Release |
Enable/disable the release phase of the modulation envelope . When disabled, the envelope only uses Attack, Decay, and Sustain phases |
ADSR Explained
Attack (A) |
Time it takes for the sound to reach full volume after pressing a key |
|---|---|
Decay (D) |
Time it takes to fall from the peak to the sustain level |
Sustain (S) |
Volume level maintained while the key is held |
Release (R) |
Time for the sound to fade out after releasing the key |
Short attack/release times are good for percussive sounds; longer settings suit pads and atmospheric textures.
LFO

An LFO is a slow waveform that can modulate parameters automatically—such as volume, pan, pitch, or mix.
Waveform Selection |
LFO waveform types:
|
|---|---|
Rate (Speed) |
Modulation speed. When not synced: 0.01-500 Hz ( at normalized 0.25). When synced to tempo: quantized to note durations from 1/256 to 4/1 bars |
Sync |
Enable tempo synchronization. When enabled, rate is quantized to musical note values; when disabled, rate is in Hz |
Retrigger |
Whether the LFO retriggers on each new note |
Phase Offset |
Starting phase position of the LFO waveform (0-1). Useful for offsetting modulation timing |
Destination |
The target parameter to be modulated (e.g., WT Mix, Pitch, Pan, Gain, Stereo Detune) |
Intensity |
Controls how much the LFO affects the target parameter |
Example: Assigning the LFO to WT Mix results in automatic morphing between A and B.
Tuning
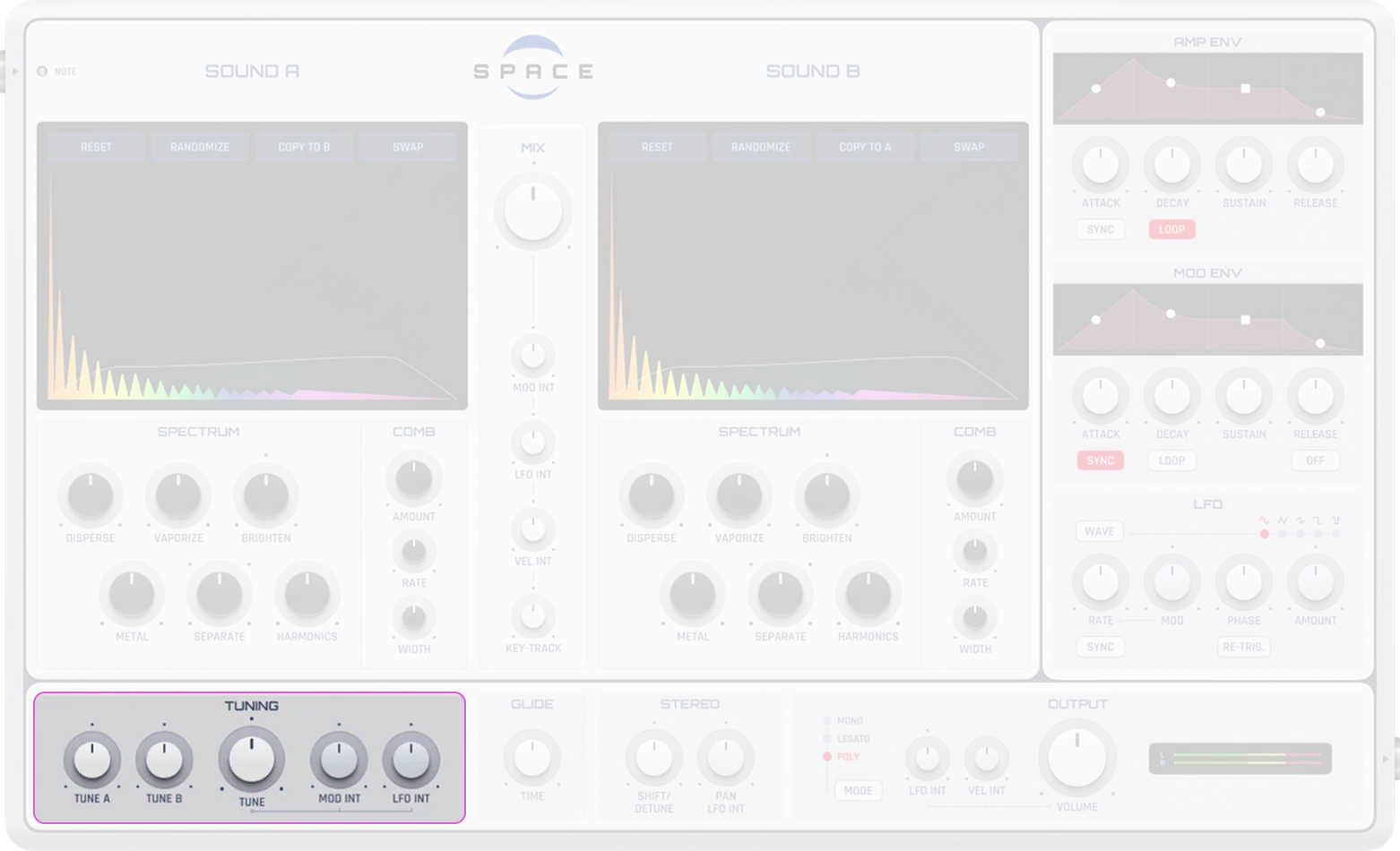
Tune A |
Adjusts the pitch of wavetable A independently (-12 to +12 semitones). Small offsets create pleasing detuning effects |
|---|---|
Tune B |
Adjusts the pitch of wavetable B independently (-12 to +12 semitones) |
Global Tune |
Shifts the pitch of the entire synth (-12 to +12 semitones). ±12 semitones = ±1 octave |
Micro Tuning |
Optional reference to a micro-tuning resource for alternative tuning systems |
Modulation
The modulation envelope and LFO can modulate various parameters. Each modulation destination has its own depth control:
Mod Env → Pitch (Tune) |
How strongly the Mod Envelope affects global pitch (-100% to 100%) |
|---|---|
Mod Env → LFO Rate |
How strongly the Mod Envelope affects LFO speed (-100% to 100%) |
Mod Env → LFO Amount |
How strongly the Mod Envelope affects LFO intensity (-100% to 100%) |
Mod Env → Mix A/B |
How strongly the Mod Envelope affects wavetable mix (-100% to 100%) |
LFO → Pitch (Tune) |
How strongly the LFO affects global pitch (-100% to 100%) |
LFO → Gain |
How strongly the LFO affects output volume (-100% to 100%) |
LFO → Mix A/B |
How strongly the LFO affects wavetable mix (-100% to 100%) |
LFO → Panning |
How strongly the LFO affects stereo panning (-100% to 100%) |
LFO → Stereo Detune |
How strongly the LFO affects stereo detune shift (-100% to 100%) |
Velocity → Gain |
How strongly note velocity affects output volume (0% to 100%) |
Velocity → Mix A/B |
How strongly note velocity affects wavetable mix (-100% to 100%) |
Keyboard → Mix A/B |
How strongly keyboard position (note pitch) affects wavetable mix (-100% to 100%) |
Useful for effects like vibrato, pitch sweeps, subtle detuning, or velocity-sensitive timbre changes.
Glide, Stereo & Output

Glide Time |
Smooth transitions between notes (0-5000 ms). Ideal for legato basses or leads. In Mono/Legato mode, notes glide if they overlap; in Poly mode, notes glide if they don’t overlap |
|---|---|
Stereo Detune Shift |
Multi-purpose parameter to widen the stereo image (-100% to 100%). Negative range (-100% to 0%): phase-shifts channels for wider perceived stereo without pitch shift. Positive range (0% to 100%): detunes voices (right channel down, left channel up) up to 12 semitones. At -100%, both voices are equal (mono) |
Output Gain |
Controls the overall output level (0-1 linear, equivalent to -∞ to 0 dB or -3 dB) |
Voice Modes (Note Play Mode) |
Play mode:
|
Practical Tips
Practical Tips
Start with a preset and tweak small things (like the envelope).
Use “Randomize” to explore new sound directions.
Listen closely to how partial adjustments affect timbre.
Use LFOs to add motion to pads or basslines.
Monitor your levels—too much output can cause distortion.
Slowly modulate the mix control for evolving and organic textures.